[Page 2] |
Multiple Choice
(1 pt each)
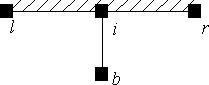
2. (seep-findiff) Which of the following is the correct finite difference formulation for the node i shown below?
a. hi = 1/3(hl + 0.5hb + hr) b. hi = 1/4(2hl + hb + 2hr) c. hi = 1/2(hl + 2hb + hr) d. hi = 1/2(0.5hl + hb + 0.5hr) e. None of the above are correct.
3. (seep-findiff) For the mesh-centered finite difference grid shown below:
which of the following is a correct representation of dh/dx from node l to node i?
a. b. c. d. e. None of the above
4. (seep-finelem) Which of the following is not true of the finite element method relative to the finite difference method?
a. You can model irregular boundaries more easily. b. You can model heterogeneous problems, while the FD method can only be used for problems with one material zone. c. It is more difficult to code. d. All of the above are true.
5. (seep-finelem) The transmissibility matrix resulting from the finite element formulation is relatively easy to solve since it is:
a. a unit matrix b. a jacobian matrix c. banded and symmetric d. triangle dominant e. none of the above
6. (seep-goveq) Which of these statements is consistent with following governing differential equation?
a. steady state b. isotropic c. external sources/sinks d. major axes of k aligned with xyz axes e. All of the above f. None of the above
7. (seep-analytical) Which of the following is not a Dupuit assumption?
a. The exit point is at the same level as the tailwater. b. The hydraulic gradient is constant along a vertical line. c. The hydraulic gradient is equal to the slope of the free water surface. d. All of the above are Dupuit assumptions.
8. (seep-finelem) The transmissibility matrix used in the formulation of the finite element equations consist of:
a. Hydraulic conductivity terms b. Geometric terms c. A combination of the above
9. (seep-goveq) For the governing equation:
which of the following conditions apply?
a. isotropic b. anisotropic c. 2D d. 3D e. steady state f. transient
10. (seep-goveq) For the governing equation:
which of the following conditions apply?
a. isotropic b. anisotropic c. internal sources and sinks d. steady state e. 2D